How to set up international domains (top-level domains, subdomains, and subfolders) for your Shopify markets
We frequently receive questions from our clients about how to configure the markets for their Shopify e-shop. While Shopify markets feature is an invaluable tool for selling internationally from a single Shopify store (read more on Cross-border selling: Choosing between Shopify Markets and multi-store Shopify structure, they require careful planning in terms of settings. In this guide, we’ll explore how to structure the domain settings for the markets and discuss the limitations associated with the setup.
Domains, top-level domains, subdomains, subfolders,…What’s the difference?
Let’s explore the differences between top-level domains, subdomains, and subfolders. Essentially, a domain serves as the web address where customers locate your online store. When you establish a new store on Shopify, it’s automatically assigned a domain containing ‘myshopify.com’, such as ‘myawesomestore.myshopify.com’.
To enhance credibility and brand identity, we highly recommended to link your store to a custom domain that reflects your brand name. You can purchase a domain directly from Shopify or from third-party providers like GoDaddy.
Top-level domains allow you to have a domain with a specific extension for each target market you wish to establish. For instance, if your root domain is ‘myawesomestore.com’, you might purchase ‘myawesomestore.de’ to target specifically the German market with a unique, country-customized domain.
Subdomains are a subset of your root domain that precedes it in the URL. For instance, in the URL europe.myawesomestore.com, ‘myawesomestore.com’ is the root domain and ‘europe’ is the subdomain.
Subfolders, on the other hand, are subdirectories within your primary domain. They’re typically the simplest and quickest option for setting up Shopify markets. For instance, if your root domain is ‘myawesomestore.com’, you can create a subfolder for Germany with German language within the URL ‘myawesomestore.com/de-de’.
So, which option should you choose? Let’s explore the settings in more detail.
What are the options of setting up the international domains for your Shopify markets?
In total, there are three possible configurations you can utilize for international markets:
- Use primary market configuration
- Use a separate domain/subdomain
- Use subfolders
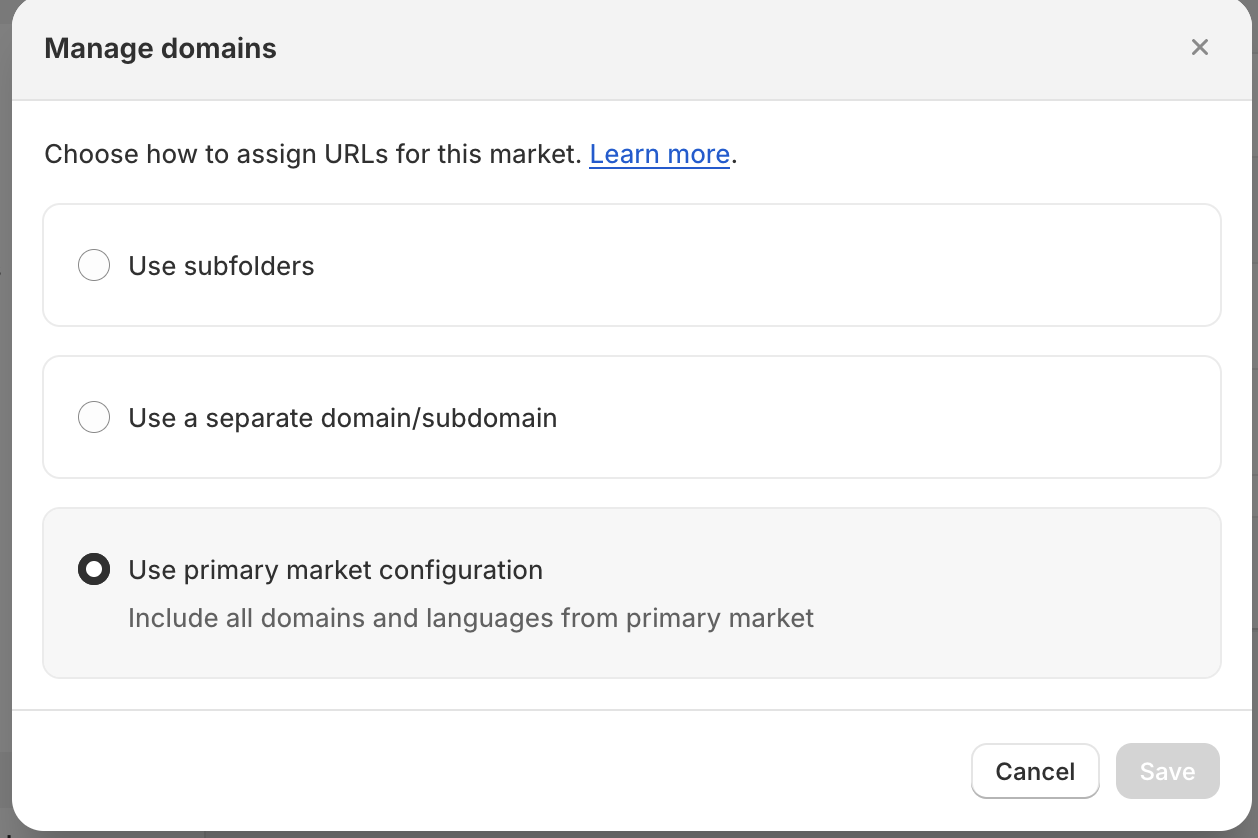
Let’s explore each option and outline some limitations that may be associated with the selected solutions. For illustration purposes, we will use the following example:
Markets:
- Primary market: Czech Republic
- International market: Germany
Langugages:
- Default language: English
- Additional language: German
Primary market configuration
In the primary market configuration, as illustrated in our example, we begin with the Czech Republic as the primary market and English as the default language. If you decide to include German in the primary market, the language will be available at ‘/de’, as shown in the screenshot below:
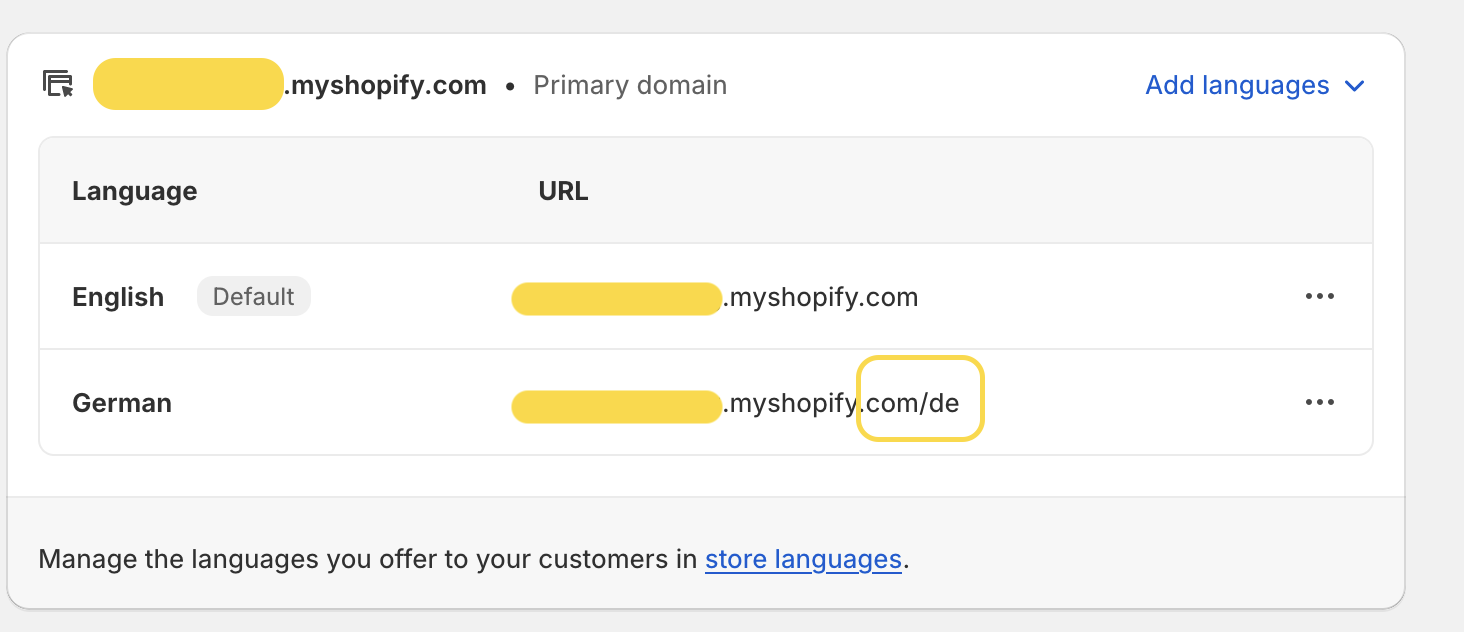
Selecting the primary domain configuration automatically replicates the exact settings of the primary market to your newly created German market. This offers the significant advantage of eliminating the need for additional configuration; everything is already set up.
Primary market configuration: Limitations and SEO
However, a major drawback of this setting emerges when you want to change the default language for your German market. Since this market utilizes the primary market configuration, any changes made to the default language will also affect the primary market.
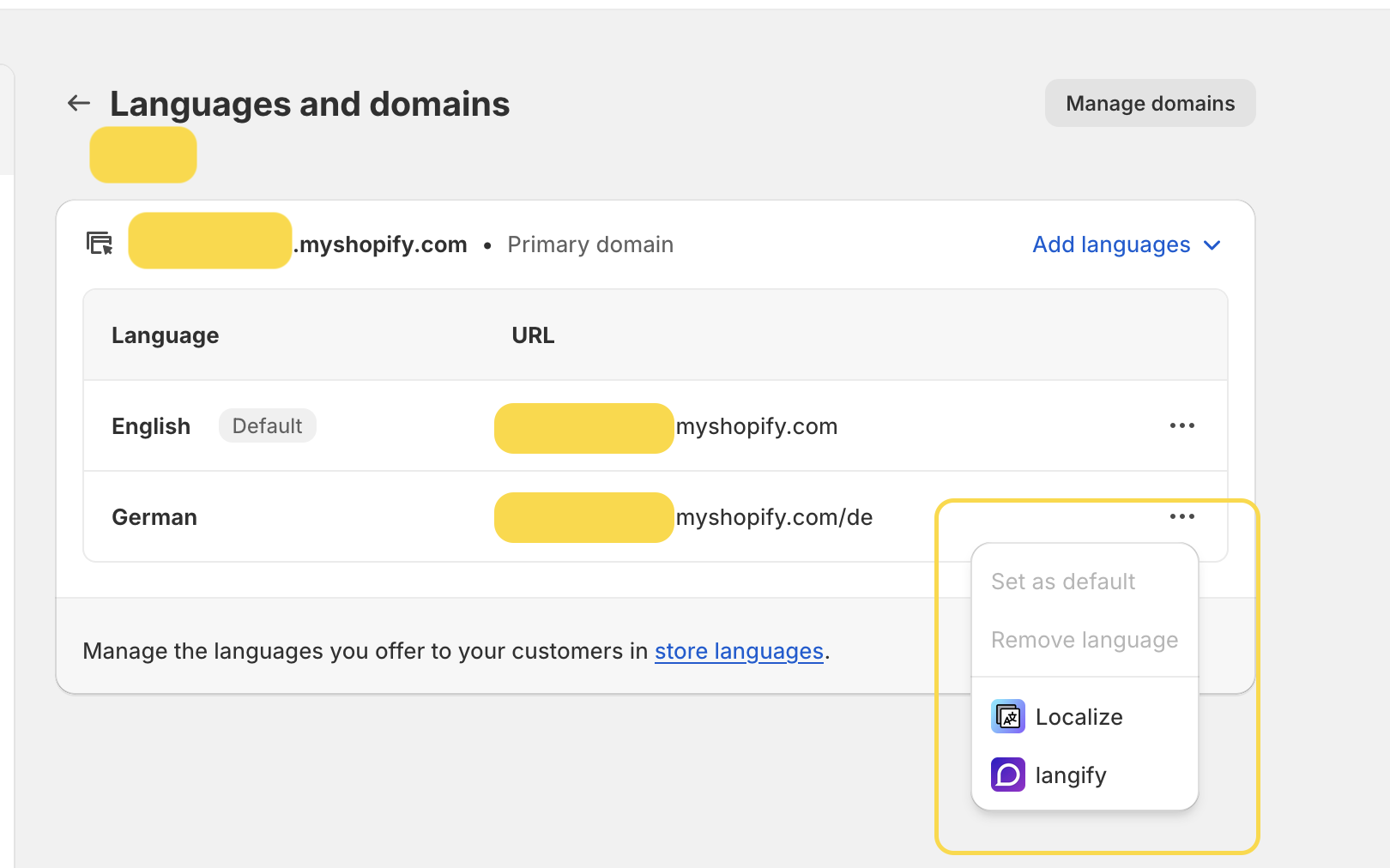
If you use a Geolocation app, it offers pop-up recommendations to your e-shop visitors, allowing them to select their country and language preferences. Nevertheless, this app has its limitations; in many instances, it sets the language based on the visitor’s browser settings beforehand, potentially restricting the ability to switch languages through the pop-up.
Since the Geolocation app will be offset later this year, you may want to explore some alternative apps such as Selector – Geolocation & Markets.
In terms of SEO, since you leverage your primary market configuration for other markets, the same URL is used for every language and currency that you set up. In other words, German version of your store is always available at myawesomestore.com/de/XYZ) no matter which market the language is assigned to (unless you use a separate country-specific domain).
Use a separate top-level domain or subdomain
Utilizing separate domains is a common tactic when expanding to other markets. Essentially, you have the same e-shop available at distinct domains specific to each market.
Before you can assign a country-specific top-level domain to a market, you need to purchase the domain (domains).
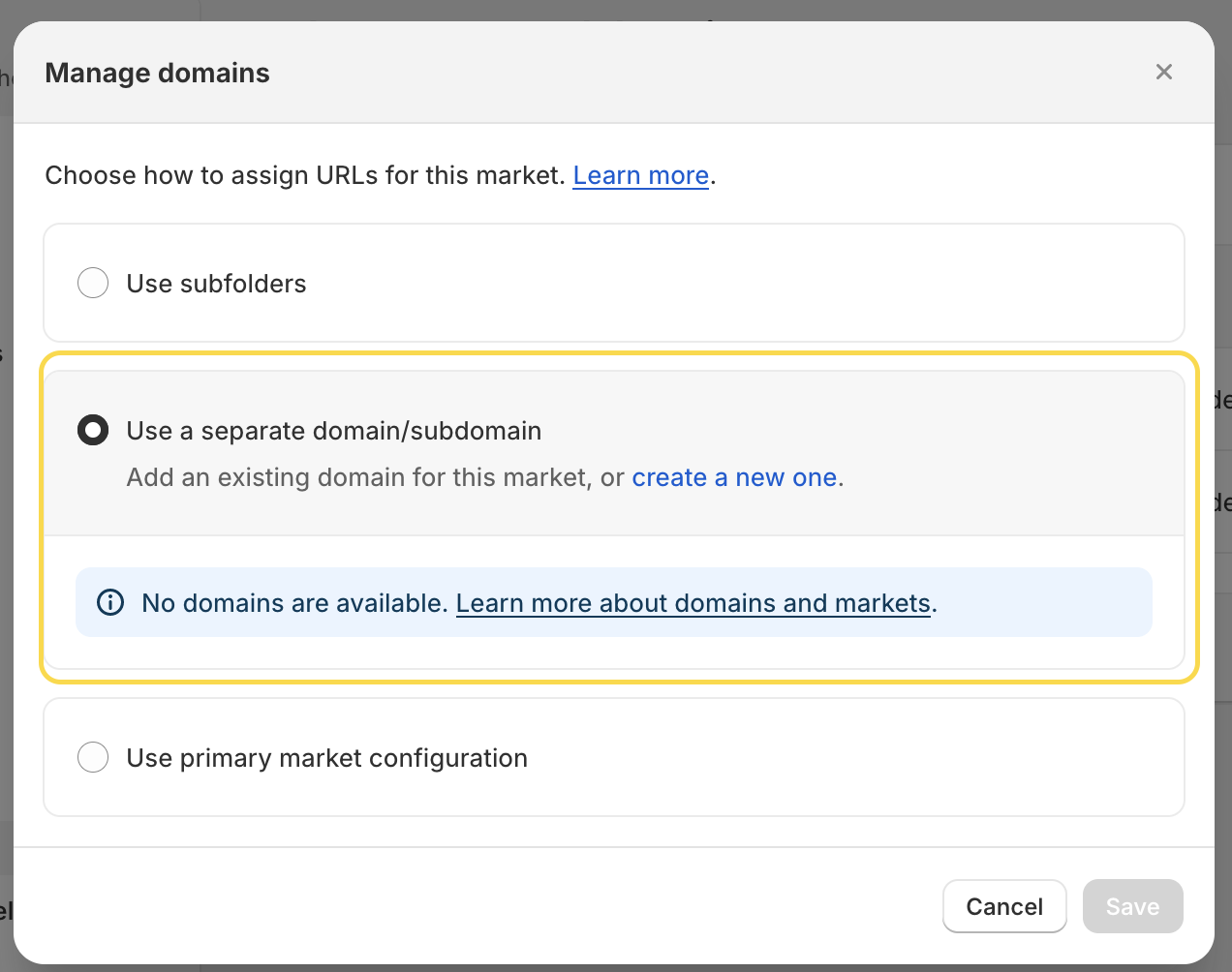
In our example, the primary domain is available under ‘myawesomestore.com’, while the German market is connected to ‘myawesomestore.de’.
Separate top-level domains: Limitations and SEO
While this setup appears professional, it also presents some limitations, particularly concerning languages, SEO, and adapting storefront content to specific markets.
For instance, you may wish to offer only English on the primary market and German on the other market, which is a feasible and optimal setup. However, challenges arise when customers in the German market want to switch to English.
Even though it’s straightforward to add English to your German market, you will notice that the English version for ‘myawesomestore.de’ will be available at ‘myawesomestore.de/en’.
If you have some basic SEO knowledge, you will notice that the content on the English version for the German market will be the same as the content on the primary market which is available at ‘myawesomestore.com’. This will require additional work to set up canonical tags between the two domains.
Moreover, market-specific (top-level) domains are entirely separate entities, each developing its own domain authority and search ranking. Therefore, this method demands the most time and effort to build up SEO.
Another disadvantage is the inability to adapt the storefront (e.g., add sections, blocks, hide some elements) for a specific market if the default language (English, in this case) isn’t available for the market you want to make changes for.
While you can localize content through a translation app (e.g., Translate & Adapt), you can’t easily customize the storefront for the market (Germany, in this case) using the Customize editor. If you wish to do so, you need to enable the default language for that market.
Similar issues arise when setting up subdomains for your markets.
Important note!
It’s important to remember that one specific domain corresponds to one market. You can’t assign, for example, ‘myawesomestore.de’ to two markets; only the primary market domain can be assigned to multiple markets using the primary market domain configuration. Thus, while this setup makes sense for various reasons, it may not be immediately clear at first glance.
Use subfolders
Using subfolders is a common method when expanding to new markets, especially if you’re not yet ready to establish country-level domains for each market.
With subfolders, you append a region-specific suffix to your URL, following the two-letter language suffix for each supported language in the market. It’s important to note that you can’t modify the initial two-letter language suffix, as it’s automatically generated based on the assigned languages for the market.
These subfolders are created within your primary domain and automatically route visitors to the appropriate URL based on their language and location preferences.
Subfolders: Limitations and SEO
In terms of SEO, subfolders leverage your primary domain, allowing your region-specific URLs to benefit from your store’s existing search ranking and domain authority. However, when you have multiple markets set up with subfolders, you may encounter duplicated language content across different URLs specific to each country or region.
For instance, if we create a subfolder for our German market to include English, the URL would be ‘myawesomestore.com/en-de’. Similarly, if you opt to add German to this market, the German language version would be accessible at ‘myawesomestore.com/de-de’.
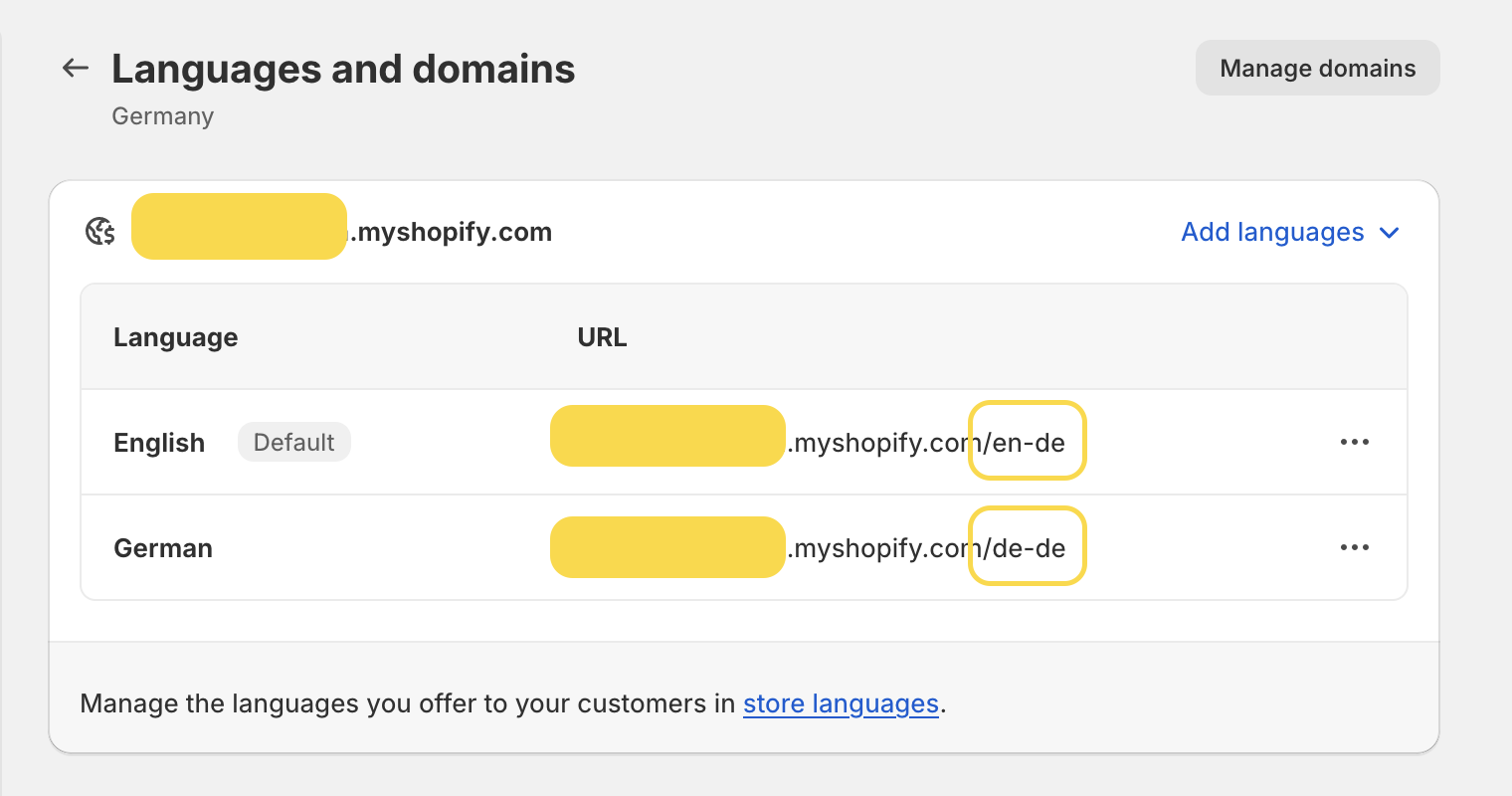
Now, if you decide to establish a separate market for Switzerland (for reasons like fixing prices, etc.), the English and German URLs for this market will be ‘myawesomestore.com/en-ch’ and ‘myawesomestore.com/de-ch’.
Thus, you’ll encounter duplicate content across multiple URLs once again.
While addressing SEO duplicate content may be necessary, it’s crucial to understand the other aspect of the setup–Shopify markets allow you to serve customers in multiple countries and languages from a single Shopify store, presenting a significant advantage (financial, administrative, and more ).
Removing a language or a market from your store
It’s important to bear in mind that utilizing e.g., subfolders, to target a specific market can lead to issues if that market (or a language assigned to that market) is later removed.
Visitors trying to access the localized version of your online store may encounter a 404 error page. To address this, you can establish redirects, as outlined in our previous article on How to Set Up Redirects on Shopify?. This guide covers manual setup, bulk import, and real subfolder redirect examples, providing solutions to prevent such errors.
Tip: Review your analytics to identify the most frequently visited localized URLs, then begin establishing redirects for these pages.
Automatic redirects (country/region and language)
In Shopify, you have the option to activate the automatic redirect feature, directing customers based on their country and browser language. However, it’s important to note that in the EU, using this feature may not be compliant with legislation, specifically the Geo-blocking regulation.
Businesses can’t block access to their website or app based on an EU customer’s location or IP address, unless permitted by national or EU law. This prohibition includes a ban on automatically redirecting EU customers to a local version of a website without their explicit consent.
Example: If a customer based in Spain wishes to access a company’s German website (i.e., website aimed at the German market), the German company cannot block access or redirect the customer to a Spanish market version of the website without the customer’s explicit consent. Even where this explicit consent is obtained, the original version of the website should still remain accessible to the customer.
Extracted from EU Geo-blocking Regulation
Wrapping things up
To sum up, setting up international domains for your markets isn’t hard technically. However, it does need some planning, especially if you want to expand to more markets. You also need to understand the limitations and problems that come with the different international domain options, especially how they affect SEO. However, at the same time, leveraging a single Shopify store allows you to seamlessly expand into new markets without the need for additional store setups
If you’re struggling to set up your domains for your Shopify store, just let us know. We’re happy to help you out.
Want to learn more about Shopify markets? Check out Cross-border selling: Choosing between Shopify Markets and multi-store Shopify structure.
